Optimizing Injection Molding Efficiency with Advanced Cooling and Process Control Technologies
In injection molding, achieving both quality and efficiency depends not only on the mold design but also on the precision of processing techniques. Among the many factors that influence part quality and cycle time, injection mold cooling system design and process control strategies play critical roles in delivering consistent, high-performance results.
The Importance of Scientific Molding Cooling Process
A well-engineered scientific molding cooling process ensures that heat is uniformly and efficiently removed from the mold cavity. This helps maintain dimensional accuracy, reduce warpage, and prevent internal stresses. By controlling the temperature profile throughout the cycle, manufacturers can achieve repeatable, stable production even in high-volume scenarios.
Efficient Mold Cooling Channels for Better Part Quality
Designing efficient mold cooling channels is essential to minimizing cooling time—the longest portion of the molding cycle. Optimized channel geometry, spacing, and layout allow for uniform cooling across complex part geometries. When cooling is poorly designed, temperature imbalance leads to defects such as sink marks, warping, or longer-than-necessary cycle times.
Precision Mold Temperature Control for Stable Production
Maintaining thermal balance in molds requires precision mold temperature control. Using temperature controllers with high accuracy, manufacturers can keep molds within a narrow range of ideal processing temperatures. This enhances surface finish, improves material flow, and prevents cosmetic issues on the final parts.
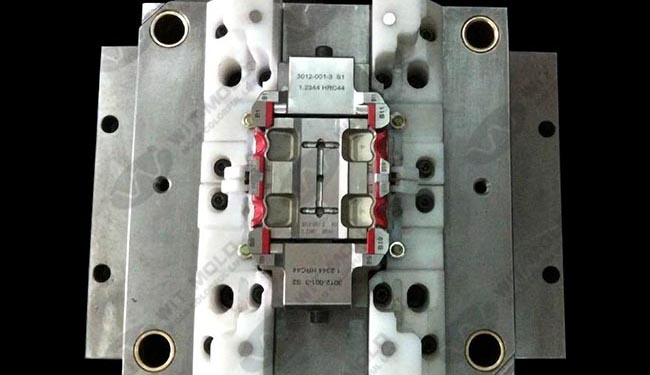
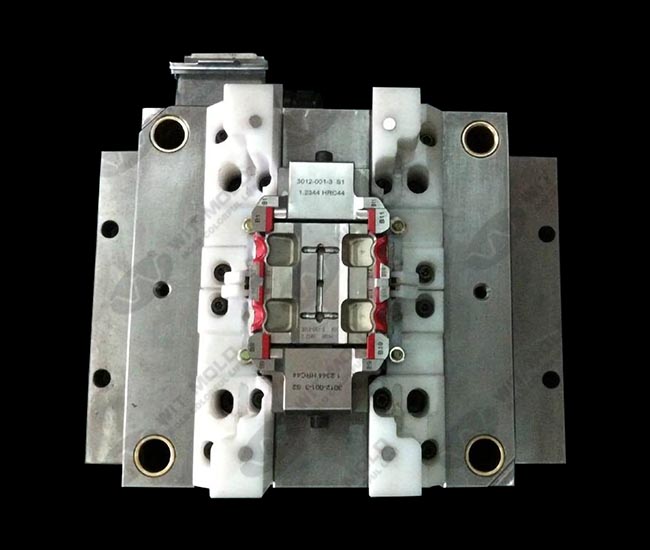
Injection Mold Cooling System Design: Balancing Speed and Quality
The heart of any efficient mold is its injection mold cooling system design. Engineers must evaluate mold materials, channel diameters, placement, and coolant flow rates to strike the right balance between rapid heat removal and structural integrity. Advanced cooling methods such as conformal cooling or beryllium copper inserts can significantly reduce cooling time and improve mold performance.
Injection Molding Cycle Time Optimization
Injection molding cycle time optimization is the key to improving productivity and reducing costs. Cooling alone often accounts for over 60% of the entire cycle. By refining cooling systems, optimizing hold pressure timing, and ensuring proper ejection, companies can drastically reduce cycle times without compromising part quality.
Injection Rate Control in Molding
Another essential parameter is injection rate control in molding. Controlling the injection speed ensures uniform filling, prevents flow lines, and reduces shear-induced degradation in polymers. Proper injection speed also influences gate freeze timing, weld line strength, and air trap elimination.
Plastic Part Design Guidelines for Manufacturability
Even with the most advanced molding systems, part quality heavily depends on design. Following proven plastic part design guidelines—such as uniform wall thickness, draft angles, and proper rib-to-wall ratios—enables efficient mold filling and cooling. Design for manufacturability (DFM) also reduces tooling revisions and accelerates time-to-market.
Mold Flow Analysis Service: Predicting Issues Before Production
Before building the mold, performing a mold flow analysis service can uncover potential design flaws and processing challenges. This simulation-driven approach evaluates material flow, cooling behavior, air traps, weld lines, and pressure distribution—allowing engineers to adjust part or mold designs before cutting steel. It’s a valuable step for reducing risk and improving first-shot success.
Conclusion
From precision mold temperature control to mold flow analysis service, every technical decision in the injection molding process impacts cycle time, part quality, and operational cost. A well-thought-out injection mold cooling system design, coupled with scientific molding cooling processes, ensures stable, high-efficiency production. By adhering to plastic part design guidelines and leveraging tools like injection rate control and cycle time optimization, manufacturers can achieve superior results in today’s competitive plastic molding landscape.










.jpg)






